Dead tooth
All content is checked by medical journalists.A tooth is dead when its interior - tooth pulp (pulp) - has died. The cause is usually an inflammation of the pulp caused by tooth decay. Read here which examinations the dentist uses to check the teeth for signs of life, which problems a dead tooth can cause and what the treatment looks like!
Nerves and vessels die
If the holes in the tooth are too deep, the tooth decay too strong, and the patient is too sloppy with oral hygiene, even a dentist can no longer save anything: the tooth dies. More precisely: the pulp, the bundle of nerves and blood vessels that supply the tooth from within, perishes. Without this care, the dentin will not survive either, so that the tooth substance gradually dies.
However, the tooth does not have to fall out immediately. In exceptional cases, a dead tooth can even go unnoticed for a long time. On the one hand, because the enamel remains stable for a while without a blood supply and, on the other hand, because a tooth without a nerve does not necessarily cause problems.
Possible signs that a tooth has died are dark discoloration, breakage of tooth substance, sensitivity to bite or, in the worst case, pain and swelling.
Inflammation as the cause
The cause of tissue death is usually an inflammation of the pulp (pulpitis). It occurs when pathogens penetrate deep holes down to the tooth nerves, most often as a result of tooth decay. Pulpitis can be extremely painful, but can sometimes be completely normal. Once the inflammation has reached the tooth nerve, it affects the entire pulp and destroys it.
If a severe toothache suddenly stops after several days, this is not a sign of spontaneous healing, but rather that the tooth nerve has died and the acute pulpitis has turned into a chronic one. Therefore, the following applies: To the dentist in good time!
The pulp is rarely damaged directly. This happens, for example, after an accident, when the tooth breaks or is knocked out. Such damage causes severe pain and can usually hardly be overlooked from a visual point of view.
Dangerous cavity
The dead pulp provides an ideal breeding ground for further bacteria. These come from the oral cavity and easily migrate into the tooth when the caries has already made its way there.
The bacteria start to rot the dead tissue. An aggressive inflammation develops (called gangrene), which is noticeable by its foul odor. Because the pathogens can easily work their way into the whole jaw, gangrene is particularly dangerous. If an inflammation at the root tip breaks through into the surrounding tissue, an abscess, the "thick cheek", occurs.
Search for signs of life
To determine whether a tooth is dead, the dentist carries out a so-called vitality test. Usually, a cotton ball is sprayed with cold spray and held against the tooth. In simple cases, a short puff of air from the water-air gun is sufficient. If the patient feels the cold stimulus, the vitality test is positive, which means: the tooth is alive.
If this test is negative, the dentist will examine the affected tooth further. For teeth with crowns or fillings, the vitality test can be unreliable and give false-negative results.
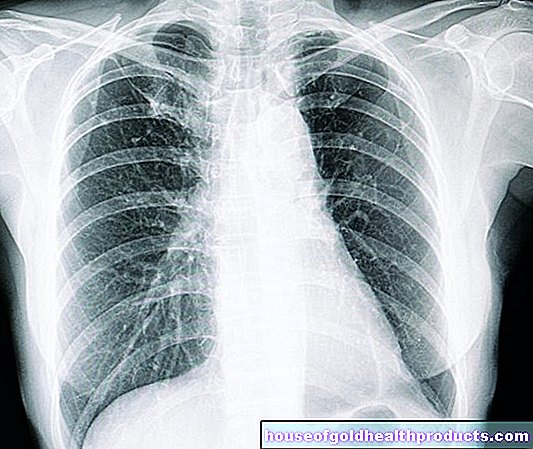
Another indication of a dead tooth is the percussion test, in which the dead tooth reacts painfully to knocking. The cause of the pain is an inflammation in the jawbone - the root tip inflammation, which surrounds the root tip the size of a pea. The jaw hurts, not the dead tooth itself. In case of doubt, an X-ray provides clarity. Chronic root tip inflammation can then be recognized by a circular change at the root tip.
The consequences
A dead tooth must be treated, otherwise there is a risk of chronic inflammation and tooth loss. If possible, the dentist will try to preserve the tooth and perform root canal treatment. The root canal is cleaned and sealed with a filling.
If the tooth cannot be saved because it is too brittle, too loose or permanently infected, there is only the last resort: the tooth is extracted (extraction). The resulting tooth gap can be closed in various ways, for example with a bridge, an implant or with a removable denture.
Tags: menshealth alternative medicine laboratory values










.jpg)