HIV test
Mareike Müller is a freelance writer in the medical department and assistant doctor for neurosurgery in Düsseldorf. She studied human medicine in Magdeburg and gained a lot of practical medical experience during her stays abroad on four different continents.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.An HIV test can be used to determine whether someone has been infected with the HI virus (HIV) - the causative agent of AIDS. In order to be able to make an exact statement, two tests are always carried out. The time of the examination is also important for a meaningful result. Read more about how a rapid test can detect HIV, what other test methods there are and where you can get an HIV test!
ICD codes for this disease: ICD codes are internationally recognized codes for medical diagnoses. They can be found, for example, in doctor's letters or on certificates of incapacity for work. Z21B23B22B24

HIV test: when and where?
An HIV test is a blood test that is used to confirm or rule out HIV infection. It is also known colloquially as the AIDS test. However, since the test detects the causative agent of AIDS, the HI virus, the term HIV test is more correct.
If you are concerned that you might have become infected with HIV, for example through unprotected sex or a broken condom, you should get tested. Even if you and your partner decide to have sex without a condom in the future, we recommend that both of you get an HIV test beforehand. The health department, family doctor, various specialists such as gynecologists and AIDS counseling centers are the right places to go. Self-tests for HIV have also been approved in Germany since October 2018.
The family doctor or specialist will first ask you in detail about your medical history (anamnesis). He will then take your blood and send it to a laboratory for further analysis. An anonymous HIV test is possible in AIDS counseling centers.
HIV test: mandatory notification
If an HIV test in the laboratory is positive, this must be reported to the Robert Koch Institute (RKI), but without naming the patient - the patient remains anonymous for the RKI. The institute collects all registration data in order to have an overview of the current spread of HIV infection in Germany.
HIV test: blood donation
HIV test procedures have been used routinely in Germany before a blood donation since 1985. The aim is to prevent the HIV virus from being transmitted to the recipient through a blood transfusion. Some people use the blood donation as a regular HIV test, which is not advisable: Apart from the fact that an HIV test can only detect an infection some time after the infection, the blood donation test is not anonymous and you will receive it from one of them positive test result sometimes no further advice. It is therefore better to go to the health department: HIV tests and AIDS counseling are offered there anonymously and free of charge.
HIV test: standard procedure
Indirect testing is usually used to detect or rule out HIV infection. Two tests are done for a reliable diagnosis:
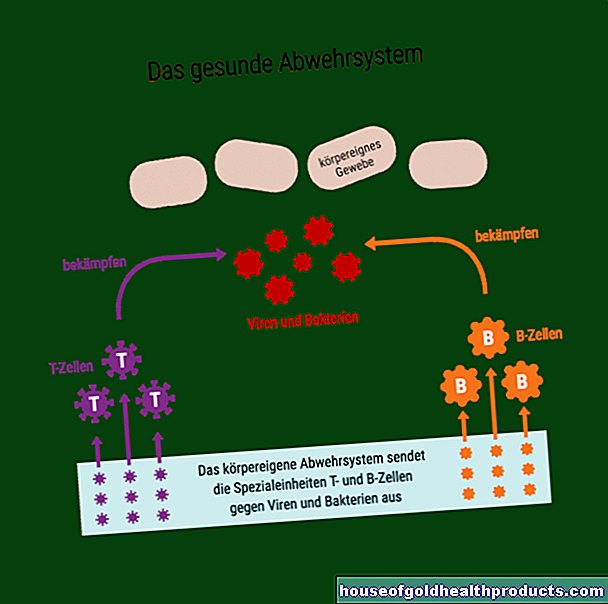
In the first test, the patient's blood is examined for antibodies against the HI virus. The body begins to produce such antibodies on average 22 days after infection. They are definitely present in the blood after three months and can then be detected in a so-called immunoassay. If antibodies against the HI virus are present, one speaks of a positive test result.
Due to the time window between infection and the formation of antibodies, a negative test can only provide information about the time before the past three months. HIV-negative does not mean that a fresh infection can be ruled out.
The examination for antibodies against HIV is called the HIV rapid test and is often incorrectly referred to colloquially as the AIDS rapid test. The HIV test takes about 30 minutes. The patient usually receives the result after a few days.
After a positive test result in the first evidence, a second test is carried out to confirm. Antigens of the virus are detected in the patient's blood. Antigens are protein structures of the virus against which the antibodies are directed. The test becomes positive six weeks after an HIV infection.
Only if a patient tests positive in both tests is they considered HIV positive.
HIV: PCR test
In individual cases, HIV infections are also detected by the laboratory using the genetic material of the virus in the blood (viral nucleic acids). The search for the viral genetic material is carried out using an HIV-PCR test. PCR stands for polymerase chain reaction: the nucleic acids are first duplicated and then broken down according to their properties. The genetic material can be detected in the blood just eleven days after infection, so that this method is used, for example, in newborns from HIV-positive mothers.
Home HIV self-test
HIV tests for at home have been available in Germany since October 2018. The advantage is that they can be carried out easily and anonymously. This can lower the inhibition threshold for a test. They are also just as meaningful as a test at the doctor's. A disadvantage of the procedure is that there is no personal consultation beforehand and, in the event of a positive test result, there is no direct professional support. If your test result is positive, visit your family doctor or an AIDS counseling center to discuss how to proceed.
HIV test: blood count not suitable
An HIV infection cannot be diagnosed with a simple blood count. The number of the individual blood cells is determined in the blood count and compared with the normal values. In the course of the HIV infection, changes in the blood count can occur, such as a decrease in the number of white blood cells (leukocytes). However, these changes are only suitable for monitoring the course of an HIV infection. A blood count cannot be used as an HIV test.
Tags: laboratory values palliative medicine Diagnosis


.jpg)












.jpg)


