Amylase
and Eva Rudolf-Müller, doctorDr. med. Andrea Reiter is a freelance writer for the medical editorial team.
More about the expertsEva Rudolf-Müller is a freelance writer in the medical team. She studied human medicine and newspaper sciences and has repeatedly worked in both areas - as a doctor in the clinic, as a reviewer, and as a medical journalist for various specialist journals. She is currently working in online journalism, where a wide range of medicine is offered to everyone.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.Amylase is an enzyme that is involved in the body's metabolism of sugar. It is found in saliva and in the secretion of the pancreas. The enzyme breaks down large sugar molecules that were ingested with food into smaller sugar units. If the pancreas is inflamed, an increased amount of amylase can be detected in the blood. Read everything you need to know about the enzyme here.
What is the amylase?
Amylase is an enzyme that breaks down large sugar molecules, making them easier to use. There are two different types of amylase in the human body that break down sugar in different places: the alpha-amylases and the beta-amylases.
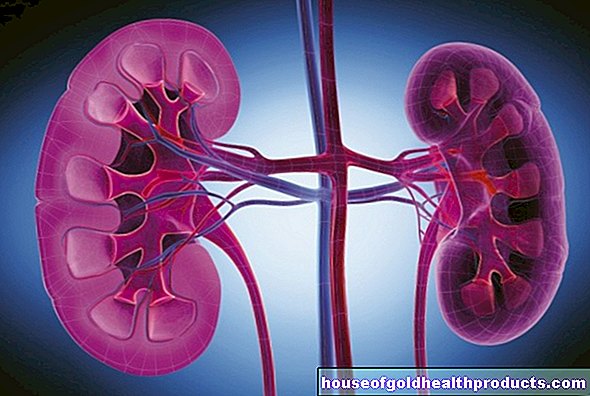
The amylase is found in the saliva of the oral cavity and in the pancreas. If sugar is ingested through food, it is split into smaller units by the salivary amylases while still in the oral cavity. The pancreas releases amylases into the small intestine. There the sugar molecules are broken down further until they can finally be absorbed into the blood through the intestinal wall.
When is the amylase determined?
The doctor has the amylase concentration in the blood determined especially when a patient is suffering from severe pain in the upper abdomen and fever. In some cases, an inflamed pancreas can be the cause of these symptoms. The determination of the total amylase concentration or the concentration of the pancreatic amylase can support this suspected diagnosis if the concentration of the amylase in the blood is increased.
A small proportion of the amylases from the digestive juice get into the blood. From there, the enzymes are excreted through the kidneys. The amylase can therefore be detected in the blood or in the urine. If the kidneys are weakened in their function, the concentration of alpha-amylase in the blood increases. Often only the concentration of pancreatic amylase in the blood is increased.
Amylase reference values
The amylase concentration in the blood serum is normally below 100 U / l (enzyme activity units = units per liter).
The following standard values apply to the amylase concentration in the urine (spontaneous urine):
|
age |
Female |
masculine |
|
up to 12 months |
20-110 U / l |
11-105 U / l |
|
1 to 16 years |
15 - 151 U / l |
11 - 162 U / l |
|
from 17 years |
<460 U / l |
<460 U / l |
The normal values can differ depending on the measurement method used. In individual cases, the standard ranges specified on the respective laboratory results always apply.
When is the amylase concentration in the blood increased?
The amylase concentration can be increased in the following cases:
- Inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis)
- Pancreatic tumors
- Inflammation of the parotid gland (for example in mumps): Here only the concentration of salivary amylase is increased
- Kidney failure (renal failure)
In the case of the diseases mentioned, in addition to the amylase, further laboratory values must be determined to confirm the diagnosis and further examinations carried out.
What to do if the amylase concentration in the blood is increased
If the level of amylase is increased, no specific disease can yet be diagnosed. Rather, further blood values must then be determined in order to clarify the cause. If the amylase is increasingly detectable in the blood due to pancreatitis, the concentration is often determined several times to monitor the progress.
Tags: dental care magazine Diseases