No e-cigarettes before the operation
Lisa Vogel studied departmental journalism with a focus on medicine and biosciences at Ansbach University and deepened her journalistic knowledge in the master's degree in multimedia information and communication. This was followed by a traineeship in the editorial team. Since September 2020 she has been writing as a freelance journalist for
More posts by Lisa Vogel All content is checked by medical journalists.E-cigarettes worsen wound healing - similar to ordinary cigarettes. Nicotine users should therefore abstain before an operation - and avoid cigarettes and their electric versions.
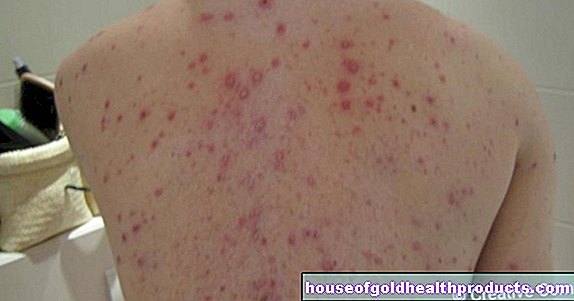
Wounds heal more poorly in smokers. This is why they have worse cards after an operation than non-smokers: there are more complications. Doctors therefore recommend that you stop smoking before a surgical procedure. Sometimes they recommend e-cigarettes. A recent study now shows that these are not a good alternative.
Rats in the nicotine vapor
Scientists working with Jeffry Spiegel from the Boston Medical Center investigated this in experiments with rats. 15 animals each sat for 30 consecutive days either in a special chamber with cigarette smoke or the vapor of an e-cigarette. The procedure was carried out twice a day for half an hour each time. 15 other animals served as controls and remained nicotine-free.
Poor wound healing in smokers and vapers
The researchers then removed flaps of skin from the animals' backs and reinserted them in the same place. In the following time she observed the wound healing. The result: Two weeks after the operation, there was hardly any difference between the "smokers" and the "steamers" but there was probably no difference to the "non-smokers" among the rodents.
For example, 68.7 percent of the transplanted tissue had died in the smoke rats, and 65.9 percent in the group that was exposed to the e-cigarette vapor. With only 51 percent tissue shrinkage, the grafts healed best in the nicotine-free control group.
"Our study supports the theory that nicotine, regardless of how it is delivered, worsens wound healing," the researchers write. Especially before surgery, the e-cigarette is therefore just as harmful as a normal cigarette.
Values like after a pack of cigarettes
In fact, the level of cotinine in the blood of smokers and steamers was almost the same. Cotinine is a substance that is produced when nicotine is broken down. Both groups of nicotine rats achieved cotinine values between 150 and 200 nanograms per milliliter of blood. In humans, these values roughly correspond to the consumption of one pack of cigarettes per day.
However, the results from animal experiments cannot be transferred one-to-one to humans, the researchers admit. This is one of the study's weaknesses. Observations of wound healing in human smokers and e-cigarette users have yet to confirm the results.
Complications from impaired wound healing
Wound healing disorders result in longer hospital stays after surgery. In addition, the risk of complications increases: the slower a wound heals, the sooner bacteria can settle and cause abscesses or blood poisoning. Wound healing disorders can also cause vascular, nerve, tendon, muscle and bone damage.
E-cigarettes are trendy
The effects of e-cigarettes on the organism have so far hardly been researched. Nevertheless, the industry is recording increasing sales. While the Association of the E-Cigarette Trade had a turnover of five million euros in 2010, it rose to 420 million euros by 2016. For 2017, the association expects another big plus. Last year, the Germans probably spent 600 million euros on the electronic glow sticks.
Tags: hospital pregnancy birth teenager




.jpg)


.jpg)






.jpg)
.jpg)

