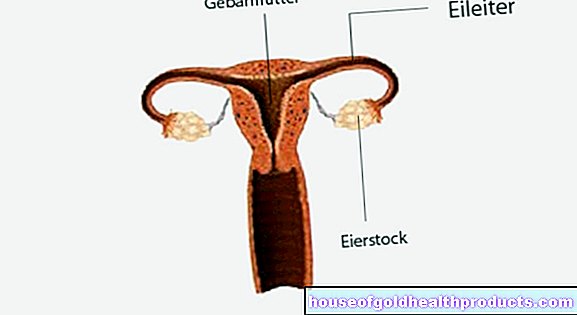
Bleeding during pregnancy
Nicole Wendler holds a PhD in biology in the field of oncology and immunology. As a medical editor, author and proofreader, she works for various publishers, for whom she presents complex and extensive medical issues in a simple, concise and logical manner.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.If there is bleeding during pregnancy, every woman is immediately concerned. However, light bleeding is not uncommon, especially in the first few weeks of pregnancy. In most cases, there is nothing to worry about either. Nevertheless, pregnant women should always take blood loss seriously. Read everything you need to know about bleeding during pregnancy here!

Menstruation or intermenstrual bleeding?
Pregnant or not? Many women make the answer to this question dependent on the absence or onset of menstruation. However, women often do not know that bleeding is relatively common, especially in the early stages of pregnancy. It is not always easy to tell what a vaginal bleeding is: the onset of your period, an early miscarriage or a harmless spotting?
So being pregnant does not rule out bleeding (with the exception of the menstrual period). In principle, any bleeding outside of menstrual bleeding is referred to as intermenstrual bleeding. Bleeding during pregnancy can be for a variety of reasons, especially between the fifth and eighth week of pregnancy. Bleeding during pregnancy is usually harmless, but it can also have a serious cause. This cannot be seen from the amount of blood. Both light and heavy bleeding during pregnancy can have serious causes. The duration of the bleeding, which can vary between hours and days, is also not really meaningful.
Pregnant: always have bleeding clarified!
Bleeding during pregnancy - whether light or heavy - should always be taken seriously. The causes are likely to vary depending on when bleeding occurs during pregnancy. You should definitely have this clarified. This is especially true if bleeding during pregnancy is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen or fever. Then you should immediately consult a doctor or the hospital! Even with a lot of bright red blood and / or great blood loss, possibly with blood clots (blood clots), urgent medical help is needed. These signs suggest a serious cause of the bleeding.
Early pregnancy: possible causes of bleeding
Early pregnancy is the phase in which the maternal organism adjusts to its new task. In the course of these changes, bleeding (intermenstrual bleeding) is relatively common. Mostly they do not come from the placenta, but from the uterine lining and pose no danger to mother or child. Bleeding in the first 20 weeks of pregnancy is considered relatively harmless with the following causes:
- Implantation bleeding: occurs on the 7th to 12th day after fertilization when the egg cell is implanted in the uterus through damage to small vessels; mostly bright red, short bleeding
- hormonal changes during pregnancy
- Cervical polyp: Polyp-related bleeding in early pregnancy can easily be mistaken for a miscarriage. Polyps promote infection and associated risks
- Infections of the vagina or cervix: not a threat to the child, but must be treated to avoid premature labor or premature delivery
- Ectopia: protrusion of the lining of the uterus onto the cervix; painless
- Contact bleeding: injury to small vessels from sex or vaginal examination; favored by infections and ectopia; usually shows up as spotting
Pregnancy and child development are generally not at risk in any of these cases. Despite the low probability, the following also applies in the early phase of pregnancy: Bleeding of any extent can be the first sign of life-threatening complications! For example, bleeding in early pregnancy can also be caused by one of the following serious triggers:
- Ectopic pregnancy: implantation of the fertilized egg in the fallopian tube; Pain in the lower abdomen, spotting, life-threatening if blood is lost in the abdomen!
- Moles of the bladder: very rare malformation of the placenta; not a viable baby
- Ovarian cysts (usually corpus luteum cysts): If they burst, blood vessels can be damaged; painful; Danger to life with heavy internal bleeding!
- Miscarriage (abortion): early abortion (up to 12th week of pregnancy) or late abortion (13th to 24th week of pregnancy)
- Cervical cancer: in the early stages mainly contact bleeding; advanced carcinomas are manifested by spotting or intermenstrual bleeding
Pregnant women should always take blood loss seriously, even in the first few weeks. A pelvic examination is essential, especially if bleeding during pregnancy is accompanied by pain, cramps or fever.
Bleeding in the second half of pregnancy
Bleeding with or without pain - the likelihood of serious complications increases in the second half of pregnancy (from the 21st week of pregnancy). This includes:
- Placenta praevia (front wall placenta): placenta incorrectly sits near or in front of the cervix; mostly painless, sudden bleeding; no to light contractions
- Premature placental detachment: placenta separates prematurely from the uterine wall (e.g. due to an accident); painful bleeding of varying degrees
- Uterine rupture: complete or partial tearing of the uterine wall; painful; Danger to life for mother and child!
- Bursting of varicose veins in the pubic or vagina area after a vaginal examination or during childbirth: life-threatening blood loss is possible
- Drawing bleeding: slight vaginal bleeding before the 35th week of pregnancy, possibly with the loss of a bloody plug of mucus; can indicate imminent premature birth!
- Late abortion, premature or stillbirth: mostly labor-like pain in the lower abdomen, lower back pain and loss of amniotic fluid
If threatening complications are ruled out, the bleeding after the 21st week of pregnancy may be harmless and not endanger the life of mother and child:
- Contact bleeding: after vaginal examination or sexual intercourse
- Placental hemorrhage: minor bleeding without labor
- "Drawing" after the 35th week of pregnancy: a bloody plug of mucus or light spotting heralds the start of labor (opening period)
How is bleeding during pregnancy clarified?
A careful examination can help the gynecologist find out whether a bleeding threatens pregnancy or the health of the mother and child. In the case of heavy bleeding during pregnancy in particular, it is crucial to identify the origin as quickly as possible. The gynecologist can already get a first impression of the seriousness of the situation with a precise palpation. Furthermore, contractions recorders (CTG) and ultrasound examinations help to search for the cause.
The pregnancy hormone hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) also reveals a lot about bleeding during pregnancy. Elevated values indicate a mole or tumor, while concentrations that are too low indicate an impending miscarriage or an ectopic pregnancy. In some cases, your gynecologist may not do a vaginal exam, as it sometimes makes the bleeding worse.
Pregnancy: what to do if you are bleeding?
If bleeding during pregnancy is judged to be harmless by the doctor, he will recommend that you rest, avoid stress and avoid sexual intercourse.
Serious bleeding during pregnancy can endanger the life of both mother and child. Bleeding must be stopped quickly, especially in the case of high blood loss, since in the worst case there is a risk of what is known as hemorrhagic shock. In the event of an impending miscarriage, contraceptive drugs and bed rest can usually prevent worse things from happening. In the event of severe complications in the second half of pregnancy, such as placenta previa, premature placenta detachment or uterine rupture, an emergency caesarean section is usually required. If bleeding during pregnancy is due to a mole, scraping may be necessary.
Tags: skin menshealth alcohol



.jpg)