impotence
and Carola Felchner, science journalistIngrid Müller is a chemist and medical journalist. She was editor-in-chief of for twelve years. Since March 2014 she has been working as a freelance journalist and author for, among others, Focus Gesundheit, the health portal ellviva.de, the publishing house living crossmedia and the health channel of rtv.de.
More about the expertsCarola Felchner is a freelance writer in the medical department and a certified training and nutrition advisor. She worked for various specialist magazines and online portals before becoming a freelance journalist in 2015. Before starting her internship, she studied translation and interpreting in Kempten and Munich.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.Impotence (erectile dysfunction) means that after an erection the penis relaxes again after a short time or does not become stiff at all. Satisfying sex is often no longer possible, although sexual desire (libido) is often still present. Potency problems increase with age. There can be psychological causes, but also illnesses such as vascular calcification or diabetes. Here you can read everything you need to know about the causes and treatment of impotence.

Brief overview
- What is impotence? The penis does not rigidify enough or long enough for satisfactory sex
- Causes: different physical and / or emotional reasons, e.g. B. cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, injuries of the erectile tissue, stress, inhibitions, depression
- Attending physician: urologist or andrologist
- Examination: Conversation, possibly also with a partner, examination of the penis and testicles, possibly also via the rectum (rectal examination), blood and urine tests, determination of hormone status
- Therapy: e.g. B. through medication, vacuum pumps, penile prostheses, surgery
- You can do that yourself: quit smoking, exercise regularly, less alcohol, keep your blood pressure and cholesterol and blood sugar levels healthy
Impotence: description
Impotence (erectile dysfunction) means that the penis is not rigid enough or that the erection cannot be sustained long enough for satisfactory sex. Doctors characterize the term impotence even more comprehensively, namely as the "inability to carry out sexual intercourse satisfactorily".
Men with impotence are not isolated cases. There are no exact figures because the number of unreported cases is very high. However, it is estimated that around five percent of men in the general population are affected. As age climbs, the risk of erectile dysfunction increases.
The level of impotence can vary greatly from man to man. Some sufferers only complain of occasional potency problems (“It sometimes doesn't work”), others report a total loss of erectile function.
Only when a sufficient erection fails to occur in around 70 percent of the attempts and the problems persist for at least six months, doctors call this "erectile dysfunction".
Forms of impotence
Doctors differentiate between two forms of impotence:
Erectile dysfunction (impotentia coeundi)
With this form of impotence, the erection is not sufficient for sexual intercourse and the penis does not become rigid enough. In addition, some men cannot control the timing of ejaculation. It comes early or delayed. Other sufferers have no ejaculation at all (anejaculation), which is extremely rare.
Infertility (impotentia generandi)
With this type of impotence a normal erection occurs and sexual intercourse can be carried out without any problems. However, the man cannot father children. Typically these men ejaculate, but there are no intact, too few, or no sperm in the semen.
Impotence: causes and possible diseases
An erection is actually a marvel: It is created through the complex interplay of blood vessels, nervous system, hormones and muscles. And each of these teammates can “lose it”.

The reasons for impotence can therefore be very different and both physical and emotional in nature. Physical causes (mostly diseases) are found in around 70 percent of men with erectile dysfunction. This is especially true in the age group 50 and over. In other men, emotional reasons are responsible for impotence.
Sometimes it is a combination of both, because psychological problems can aggravate physical limitations so much that a man can no longer at all - and that in turn scratches the male self-confidence and identity: If you don't get an erection for a long period of time, you quickly feel like half man. The fear of a renewed failure of masculinity increases the erectile dysfunction - this creates a vicious circle.
Impotence: Physical Causes
There are a number of diseases associated with erectile dysfunction. The most important are:
Cardiovascular diseases: vascular calcification (hardening of the arteries, arteriosclerosis) is the most common cause of impotence. Coronary artery disease (CHD), high blood pressure (hypertension) and high cholesterol levels (hypercholesterolemia) can also trigger erectile dysfunction. Peripheral arterial occlusive disease (PAD), the main cause of which is smoking, can also cause impotence. Obesity also has a negative effect on blood vessels.
The connection between arteriosclerosis and Imptonez is as follows: If the arteries are calcified, not enough blood reaches the penis. Conversely, the blood can flow out of the penis too quickly, sometimes both happen. The result is always that the amount of blood in the erectile tissue of the penis is no longer sufficient for a satisfactory erection.
Diabetes mellitus: Impotence is one of the most common consequences of diabetes in men. The sugar molecules are deposited on the walls of the blood vessels. As a result, not enough blood flows into the erectile tissue - the penis remains flaccid.
Hormonal disorders: The main thing that should be mentioned here is a low testosterone level. If not enough of the male sex hormone is produced or released, this weakens the ability to have an erection.
Neurological diseases: In order for an erection to occur, nerve signals must be sent from the brain to the penis. Nervous diseases such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, a stroke or tumors can interfere with the transmission of signals.
Damage to the spinal cord: disorders of the reflex responsible for erection can lead to impotence. This can be observed, for example, with paraplegia. But a herniated disc can also impair the transmission of the nerve impulses necessary for an erection.
Surgical interventions: During operations in the pelvic area (such as prostate cancer), the nerve tracts to and from the penis can be damaged. Impotence is then a common consequence.
Injuries: Injuries to the erectile tissue or the penis can prevent the limb from becoming stiff during sexual arousal.
Genital malformations: They can also be responsible for impotence.
Impotence: Mental Causes
In some of the patients, the cause of impotence is purely psychological, especially in younger men. Sexologists and psychologists see potency problems primarily as encrypted messages from body and soul. The following emotional factors can be behind when the penis strikes:
- depression
- Stress, pressure to perform
- Inhibitions, fears
- lack of self-confidence
- Protest against the "having to be a strong man"
- Partnership conflicts
- Personality conflicts, e.g. B. an unacknowledged homosexuality
Other causes
Certain drugs can also cause erectile dysfunction, including medicines for cardiovascular diseases such as beta-blockers - they lower blood pressure.
Excessive and permanently high alcohol consumption attacks the nerves in the brain and spinal cord and especially damages the nerve endings (polyneuropathy). This can also lead to impotence.
Impotence: When Should You See a Doctor?
Men who suffer from impotence for several weeks should definitely consult a doctor. Because the potency problems can be an early sign of a chronic disease, such as diabetes. If left untreated, these can become a serious health hazard. So overcome your shyness and see a doctor early if you have an erectile dysfunction!
Impotence: what does the doctor do?
The first port of call for erectile dysfunction is a urologist or andrologist. To clarify the impotence, a detailed discussion about the medical history (anamnesis) is necessary. The doctor must also ask you very personal questions, including about your sex life. Sometimes this is followed by a conversation with your partner. You should also tell your doctor about all the medications you are taking - regardless of whether they require a prescription or not. Because some drugs can cause impotence.
Investigations
The next step is to clarify the underlying causes of erectile dysfunction. It starts with an examination of the penis and testicles. A manual examination of the rectum is also recommended (digital rectal examination).This can be used to detect enlarged prostates, which can also cause erectile dysfunction.
The diagnosis of impotence also includes blood pressure and pulse measurements, as well as blood and urine tests. Among other things, the doctor will determine your hormonal status. In special cases he will also examine the nerves of the pelvic floor neurologically. In men with impotence who are older than 45 years, the blood may also be tested for signs of prostate cancer.
For a reliable diagnosis of erectile dysfunction, ultrasound examinations of the blood vessels of the penis at rest - and sometimes also after the injection of an erectile drug.
With the help of a simple device, the degree of swelling of the penis can be measured at night (tumescence measurement, NPTR measurement). It provides clues as to the type of impotence present. If spontaneous erections can be detected during sleep, this suggests that the erection mechanism basically works.
treatment
There are a number of individual therapy options for impotence. Which method is the right one in each individual case depends on the cause of the erectile dysfunction and the attitude of the man to various forms of therapy. However, one must be aware that most treatment approaches only treat impotence, but not eliminate its causes. Basically: The earlier you start with it, the higher the chances of success of an impotence treatment. The decisive factor is whether the disease underlying impotence can be treated or not.
Medication: Among the drugs against impotence, the so-called PDE-5 inhibitors are the first choice therapy. They block the enzyme phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE-5). This relaxes the penis muscles, the blood vessels can expand better and the erectile tissue fill with blood. It only works when the man is sexually aroused. The PDE-5 inhibitors include the active ingredients avanafil, sildenafil, tadalafil and vardenafil. They differ primarily with regard to the onset of action and the duration of action.
If PDE-5 inhibitors do not help or if they are not allowed to be used (for example in the case of severe cardiovascular disease or taking blood pressure lowerers), the preparation yohimbine may increase potency.
Hormone administration: Adding the male sex hormone testosterone can help in some cases of impotence. When such a therapy makes sense depends on the case in hand and should be decided jointly by the doctor and patient.
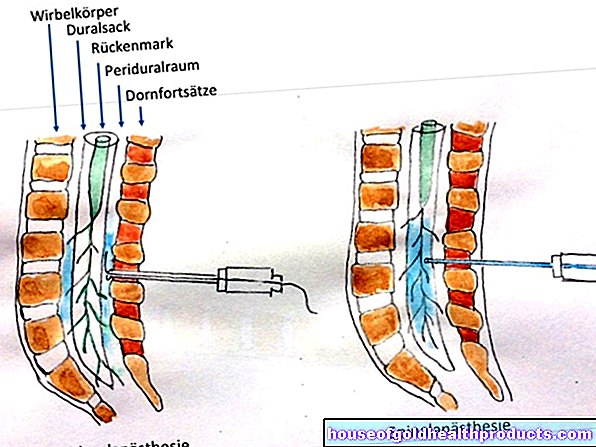
Cavernous Injection Therapy (SKAT) / Transurethale Application (MUSE): These two therapies help patients with impotence for whom tablets are not suitable. Preparations with vasodilator and blood flow enhancing prostaglandin E1 are used here. It is either injected directly into the erectile tissue of the penis with a needle (SKAT) or, as a separate preparation, it is pressed into the urethral opening at the tip of the penis using an applicator (MUSE). Administration directly into the erectile tissue is more effective, but also has more side effects.
Vacuum pump: A vacuum is created in the vacuum pump that sucks blood into the penis and temporarily remedies erectile dysfunction. A striped ring around the base of the penis prevents the blood from flowing out of the erectile tissue too quickly after an erection has been achieved.
Penile prostheses: penile prostheses should only be implanted in men with impotence if all other methods have failed - because the procedure is final.
Operations: Vascular impotence can also be treated surgically. Such interventions are risky and not very promising.
Psychological procedures: If you have impotence, use the possibility of psychological counseling. Sexual counseling and sex education as well as behavioral and conversation therapy are generally recommended for impotence. Even if there are only organic reasons for the erection problems, many men plague themselves with fears, experience changes in their partnership and thus in their social environment. Counseling can provide a lot of food for thought in order to better deal with impotence.
Doubtful and dangerous potency aids
Do not try to get the impotence under control yourself with drugs or dubious aphrodisiacs from the sex shop. Erectile dysfunction is often an important early warning sign of serious illnesses that are otherwise easily overlooked. Only a doctor can find out the cause of impotence and treat it effectively.
Pay particular attention to network offers! Stay away from illegal internet offers that deliver prescription drugs for treating impotence without a prescription. Such products are often ineffective because they only contain baking powder or flour, for example. Then you threw your money out the window. Some illegal sexual enhancers are even dangerous because they contain toxins. This not only harms your wallet, but also your health!
But even if you can get real impotence drugs on the internet, keep in mind that these can have serious side effects, like PDE-5 inhibitors in cardiovascular diseases. The preparations should therefore only be taken on medical advice and under medical supervision.
If side effects occur after using illegally sold prescription drugs, you also have no liability claims against the manufacturer. For orders from abroad, the package can also be confiscated by customs - and you will get nothing.
You can do that yourself
In the case of erectile dysfunction, it is always advisable to first improve your lifestyle:
- Stop smoking
- Weight reduction with excess kilos
- regular exercise and exercise
- Normalization of high blood sugar levels
- Normalization of high blood pressure and cholesterol levels
- Reduction in alcohol consumption
In the meantime, there is increasing evidence that such measures not only have a positive effect on general health, but also the ability to function erectile and thus can help against impotence.
Tags: skin care alcohol home remedies