Debridement
All content is checked by medical journalists.Debridement is usually the surgical cleaning of a wound. This procedure removes dead tissue and plaque - it is also known as a wound toilet. After cleaning, the wound can heal better. Read all about the procedure, when it is done, and the risks involved.

What is a debridement?
Debridement (also called debridement) is used to remove dead or infected tissue and foreign bodies. This enables or accelerates wound healing. Debridement also prevents the infection from spreading. Toxins, such as those produced after burns, do not get into the organism.
Tissue to be debridemented must be adequately supplied with blood. Otherwise wound healing is not possible and the tissue can no longer be saved. An amputation may be necessary.
When do you perform debridement?
Doctors always perform debridement when the body's own wound healing does not start by itself or is proceeding too slowly. Debridement is often necessary for the following diseases or injuries:
- Wound infections: preventing the spread of pathogens
- Circulatory disorders
- Pressure ulcers (pressure ulcers)
- Tissue crushing after accidents
- Large bruise in the wound area
- Foreign body in the wound
- Severe burns or frostbite
- Lack of scar tissue formation
What do you do with a debridement?
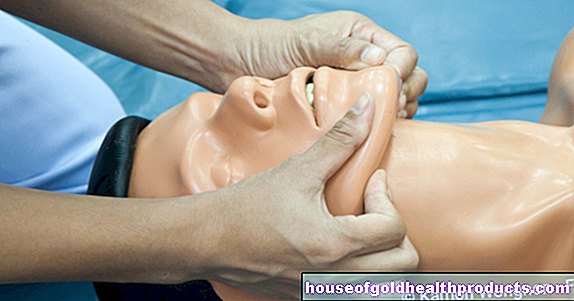
The most frequently used and fastest method is surgical debridement. The surgeon removes all dead and infected tissue from the wound - in the case of larger injuries, usually under general anesthesia - with surgical instruments (scalpel, sharp spoon). Wound coverings are also completely removed.
Surgical debridement offers the advantage that inflammatory cells are washed into the wound as a result of the injury, which makes an important contribution to healing.
In addition, a negative pressure can be generated on the wound, which improves the drainage of the wound water and additionally supports the healing process. To do this, a sterile sponge is placed on the wound, which is connected with a plastic tube to a device that generates the negative pressure.
Enzymatic debridement
Certain enzymes accelerate wound healing in long-standing wounds. These split different proteins that are in the wound coverings and in dead tissue. Only after this scab has broken down does adequate scar tissue form. Due to the lengthy treatment, doctors rarely make use of this option. In addition, it usually cannot replace surgical debridement.
Physical debridement
With the help of dry or moistened sterile compresses or wound irrigation solutions, wound coverings can be easily removed. Nursing staff perform this so-called physical debridement, among other things, when changing dressings on a daily basis. However, the method is quite painful and can damage scar tissue that has already formed.
Ultrasonic debridement is a further development: special wound gels are vibrated by ultrasound, which transports plaque and dead cells out of the wound.
Autolytic debridement
This form of debridement promotes the release of the body's own enzymes through gel-like wound dressings (hydrocolloid dressing), which break down wound coverings in a similar way to enzymatic debridement. The moist environment corresponds to the natural wound conditions, which is why more inflammatory cells migrate into the tissue and stimulate scar formation.
Biosurgical debridement
In this method, the doctor places special fly larvae in the wound, which feed on dead tissue. The fly saliva contains enzymes that break down the scab and kill bacteria. The method is painless for the patient.
What are the risks of debridement?
During surgical debridement, nerves in the wound area can be injured, sensory disturbances or paralysis can result. If blood vessels are injured, bleeding can occur.
Since the wound surface is always enlarged in the case of a debridement, there is an increased risk of bacterial infections, which usually have to be corrected by further surgical interventions.
If the surgeon has to remove so much tissue that the opposite wound edges can no longer grow together, the wound is closed with a skin flap that is removed from the patient's buttocks, thighs or back and transplanted during a second operation.
What do I have to consider after a debridement?
Do not put pressure on the wound after debridement. When showering, you should wear a special shower plaster over the wound so that no germs get into the wound with the water.It is best to talk to the nurses who will help you with personal hygiene. If you suddenly feel pain in the wound area after debridement or notice a soaked or bloody bandage, you should inform your doctor.
Tags: organ systems stress eyes








.jpg)